Muscle Strain? Avoid These 5 Mistakes (So You Can Heal Faster)
- Marissa Oxenford, PT, DPT

- Dec 2, 2025
- 4 min read

What Is a Muscle Strain?
A muscle strain is a muscle-specific injury that happens when a muscle is stretched too far, too fast, or too forcefully beyond what it can handle. When this occurs, some of the fibers that make up the muscle become irritated, inflamed, or partially torn.
Muscle strains occur across all types of athletes and even in everyday activity. Understanding what a strain is (and what it isn’t) is the first step to recovering quickly and safely.

Common Ways Muscle Strains Happen
Muscle strains often occur during:
1. Fast or explosive movements
Examples:
Sprints
Heavy lifting
Olympic lifts
Sudden change-of-direction
These movements place high force on muscle fibers very quickly, sometimes beyond their capacity.
2. Overstretching during controlled movement
Even slow tempo work (like a deep RDL or split squat) can cause a strain if the muscle is pushed past its flexibility limit.
3. Underlying contributing factors
A muscle is more likely to strain when:
It’s pushed beyond its strength, speed, or mobility capacity
It’s not properly warmed up
There is muscle imbalance or compensation
The tissue is fatigued or overworked
In most cases, a strain isn’t random — it’s a sign that something wasn’t fully prepared for the demand placed on it.
How Do You Know If You Have a Muscle Strain?
Here are the most common symptoms of a muscle strain:
Sudden sharp pain during activity
Pain that increases with stretching
Pain when contracting the muscle
Tightness or pulling that doesn’t “loosen up” with movement
Swelling, bruising, or tenderness (in moderate to severe strains)
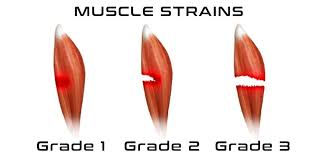
Muscle Strain Healing Timeline
Healing depends on the severity of the strain:
Grade 1 Muscle Strain (Mild)
Minor tearing or irritation
Healing Time: ~2–4 weeks
Grade 2 Muscle Strain (Moderate)
Partial muscle fiber tearing
Healing Time: ~4–8 weeks
Grade 3 Muscle Strain (Severe)
Full tear or near-complete tear
May require surgery
Healing Time: 6–8+ months if surgery is needed
These timelines assume proper care — not rest, icing, and hoping for the best.
The 5 Mistakes That Slow Muscle Strain Recovery
Mistake #1: Icing the Muscle Strain Immediately
Ice can reduce pain, but it decreases blood flow — and blood flow is what delivers healing nutrients.
So while ice doesn't completely shut down blood flow, it does significantly reduce circulation, slowing the healing process.
✔ When ice may still be useful
When swelling has been uncontrolled for a prolonged period of time.
✔ Better alternative
Use gentle movement and light heat (if appropriate) to promote blood flow. Controlled mobility speeds up healing far more effectively than numbing tissue with ice.
Mistake #2: Stretching the Tight, Painful Area
After a strain, the muscle often feels “tight.” But that tightness is protective guarding, not true stiffness.
Because strains often occur due to overstretching, pulling it further can:
Delay healing
Increase tearing
Increase inflammation
✔ What to do instead
Light mobility
Gentle isometrics
Gradual loading
These help the tissue reorganize and heal without re-injury.
Mistake #3: Complete Rest
Total rest reduces circulation, weakens surrounding muscles, and slows recovery.
✔ When rest of the injury site may be needed
Significant swelling
Severe pain even without movement
Suspected Grade 2–3 strain
✔ What “safe movement” looks like
For a hamstring strain, for example:
Light, slow walking
Pain-free hip mobility
Glute activation
Isometric holds
A PT can help determine what level of movement is appropriate based on injury severity.

Mistake #4: Ignoring the Injury and “Pushing Through It”
This is one of the fastest ways to turn a mild strain into a severe one.
✔ How ignoring it causes more damage
Weak, healing fibers can’t tolerate high load. Adding explosive or high-intensity training too soon can:
Increase tearing
Cause compensation injuries
Turn a Grade 1 strain into a Grade 2 or Grade 3
✔ What ignoring looks like
Continuing regular training
Stretching through pain
Skipping warm-ups
Only using random Google or social-media rehab videos
✔ What proper care looks like
Correct diagnosis
A structured loading plan
A progressive strength and mobility program
Activity modification when needed
Mistake #5: Not Addressing the Root Cause (“The Why”)
This is the mistake that leads to repeat muscle strains.
Most strains are preventable and happen due to:
Mobility deficits
Strength imbalances
Poor warm-up
Overuse or fatigue
Capacity mismatch (speed/strength output > tissue preparedness)
Compensation from another issue
✔ How to assess root cause
A PT evaluation can analyze:
Range of motion
Strength asymmetry
Movement mechanics
Technique during lifts or sport-specific skills
Tissue quality
Warm-up quality, mobility capacity, strength balance, and recovery all play a huge role in prevention.
Final Thoughts: You Can Heal Faster — If You Avoid These Mistakes
Most muscle strains don’t need to sideline you for weeks or months. With the right plan, you can recover faster, reduce pain, and return to training confidently.
If you're dealing with a strain — or keep getting the same nagging injury — We can help you identify what’s going on, address the root cause, and guide you safely back to performance.
Learn more about Muscle Strains by listening to our Podcast Episode HERE!
Don't forget to subscribe ;)
Local to Tampa, FL and dealing with a muscle strain yourself, or any other nagging injury, and you want to figure out your next steps, BOOK A FREE PHONE CONSULT today and let's chat!
No a phone person? That's ok! REQUEST AN APPOINTMENT and we will be in touch shortly!
Talk to you soon,
Redemption Physical Therapy
YouTube: Redemption Physical Therapy




Comments